
A Little “Customer Voyeurism”…
Last week, my family and I took a vacation to visit some of my in-laws in California. For those of you who know me, you’ll appreciate the fact that any trip for me is an opportunity for a little “customer voyeurism.” That is, I very much enjoy watching exchanges between customers and service providers, whether I am engaged in the transaction or not, largely because they provide me with a wealth of perspectives that serve to validate and augment the many years of performance data, benchmarks and trends I’ve collected in my research and client engagements. So, while spending part of my vacation documenting the customer experiences of myself and others may seem a little weird to some of you, I was not about to miss the insights that would undoubtedly be generated by this seven-day excursion into the depths of airline, restaurant, amusement park, golf course, and taxicab servicing processes.
Like most, this trip did not disappoint (as far as the volume of insights and “take-aways” go). While there was no shortage of examples on both the good and bad aspects of the customer experience (too many to share in one post), I decided to zero-in on what I am finding to be an interesting phenomenon, i.e., the apparent implication of company size on customer satisfaction, engagement, and perception.
Here’s what the data from my little informal research gig told me:
- The vast majority of transactions (experiences) appeared to be “issue neutral”- apparently meeting expectations of the customer (deduced through a lack of a visible change in emotion on either side)…Note that I use the word expectations deliberately since I believe many customer’s expectations are considerably lower than in past years. Hence, delivering against a “bar” that is set very low is not likely to produce a lot of emotion other than resignation or apathy.
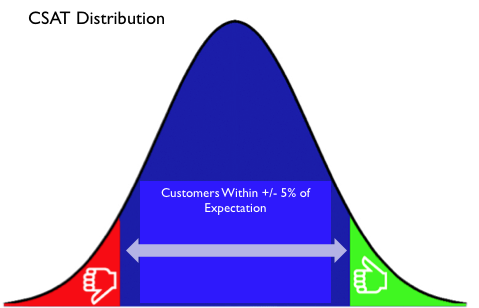 While they were few and far between, there were failures and successes on “the fringes” of the distribution. I’ve shown a simple example of what I mean, although I believe actual research on a broader set of experiences would probably show that the distribution is anything but “normal” /gaussian (i.e. these days it is likely skewed to the left assuming customers still have some semblance of expectation (hope) of good service, which of course, is debatable (I’ll leave that for another post).
While they were few and far between, there were failures and successes on “the fringes” of the distribution. I’ve shown a simple example of what I mean, although I believe actual research on a broader set of experiences would probably show that the distribution is anything but “normal” /gaussian (i.e. these days it is likely skewed to the left assuming customers still have some semblance of expectation (hope) of good service, which of course, is debatable (I’ll leave that for another post).
That notwithstanding, If we were plotting this data, we’d be talking about a data distribution with some range of values that characterize the majority of observations, and a small number of significant negative (small in number, but “intense” as far as generating negative emotion…and what our lean or six sigma brethren would call “failures”), and significant positive experiences (pure, but perhaps unexpected, delight- or what my friend Stan Phelp’s at “9 Inch Marketing” (no relationship to the title of this post!!!) likes to call “Lagniappe” in his “purple goldfish” project), at the “tails” of the distribution.
In my experience on this trip, the above distribution was more in line with my observations in that there were probably an equal number of positive and negative experiences on each side of the norm, along with a similar proportion of significant negative and positive experiences on the fringes. The following however, was particularly noteworthy.Most
-
- (90%+) of the really poor exchanges (generating a fairly clear display of emotion from neutral, to visibly “pissed”) occurred with what I would call larger more established companies
- Most (60%+) of the really positive exchanges (generating what we might refer to as “delight”, or as Stan Phelps likes to refer to it, “customer lagniappe”) occurred with small companies (“Mom and Pops” and/ or specialty stores in cottage industries)
I’ll say again, that throughout this trip, I was only able to observe several dozen transactions between a variety of customers and service providers, including those encountered by yours truly. And while this hardly qualifies as a statistically relevant sample, and falls well shy of what I would consider a rigorous research approach, it served its purpose of identifying a subject worthy of some debate and dialogue.
Why Size Matters…
Why does the above phenomenon occur? Hard to say exactly, but my hunch would be that it has a lot to do with the history and evolution of these organizations. Clearly the smaller “niche players” have a vital need to differentiate and compete, since many lack the market size and scale to do so “naturally.” And while service is one way to accomplish that differentiation, you’d expect some real “over-achievement” in this segment. In fact, the brand identity of many of these companies is directly tied to some “exceptional” aspect of their product or service offering (e.g. the special touch in the packaging, the handwritten thank-you note, or similar gestures). It’s a necessity for these companies, and when they realize they’ve stumbled onto a differentiator (deliberately or by accident), it’s relatively easy to clone and replicate.
No so much with the larger players. Sadly, many of the companies causing the above “grief” were once viewed as nimble and leaders in CS space (think wireless providers, regional airlines, etc.). Not anymore. Sure, they all have their positive exceptions, but with these companies, many of the interactions have been routinized into their operational processes and automated systems, most of which were built on the foundation of operational and technology excellence, rather than on the basis of what differentiated their service to begin with. That leaves the only opportunity for real customer “delight” in the hands of standout employees operating “on the margin”, often operating outside of the process to either strengthen the exchange or recover from a process-inflicted problem. While scale and size should be an advantage, many of these companies have allowed it to become a disadvantage.
That is not to say that the larger companies did not generate some level of delight, and that the smaller companies didn’t generate some significant failures. For example, I did get a “call back” from a CSR after a “disconnect” from a rather large company call center, which was nice to see for a change. I also experienced what I’d call a “super save” from an airport employee to avert what could have been a significant failure. And the small companies, on occasion did generate some negative experiences. Interestingly though, my tendency was to “forget” these failures quicker, giving them the benefit of the doubt for not having all of the CRM tools and technologies that larger companies have at their disposal. But in the end, my observations were my observations, and the trends were notable.
Breaking the Trend…
Given the above reality that size does apparently influence customer experience, and recognizing that “shrinking the company” is not the desired path to breaking that trend, companies that are increasing in size and growth need to be especially vigilant in five key areas:
- How we measure success – We need to once and for all get beyond the measurement of general perception, because it tells us little about performance against real customer desires, and tells us virtually nothing about what is really happening on the margin.
- How we view risk and failure – When we think of risk and failure, we normally think of manufacturing or operational processes, not customer processes. We need to get beyond the notion that 95% satisfaction is acceptable, and into the zone of limiting the number and magnitude of breakdowns on the margin (what are now viewed as exceptions or acceptable tolerance. Think: How would a Six Sigma or Lean driven manufacturing process view this challenge?
- How we build our processes – We can start by changing from a functional to a market-driven approach to building our processes and systems. Most systems today are built to optimize cost and effectiveness at the transaction level, rather than the customer level.
- How we staff and develop our employees – It is becoming harder and harder to find retainable employees that come “hardwired” with a strong CEM mindset. Finding and retaining them in large numbers is virtually impossible these days given employee demographics and market conditions. We need to look to other industries and functions to learn how to build and clone the human capital skills to support and enable the above processes.
- How we manage and reinforce performance – In support of all of the above, we need to change what we teach, how we lead, what we observe, how we motivate, and what we elect to reward in terms of its orientation toward CEM excellence.
The old adage…think globally, act locally…seems to have some relevance here. I am firmly of the belief that the notion of large size, scale and growth can effectively co-exist with high levels of service, at the norm and the margin. It just takes work on the front end to design the right foundation to make it all work.
Author: Bob Champagne is Managing Partner of onVector Consulting Group, a privately held international management consulting organization specializing in the design and deployment of Performance Management tools, systems, and solutions. Bob has over 25 years of Performance Management experience and has consulted with hundreds of companies across numerous industries and geographies. Bob can be contacted at bob.champagne@onvectorconsulting.com



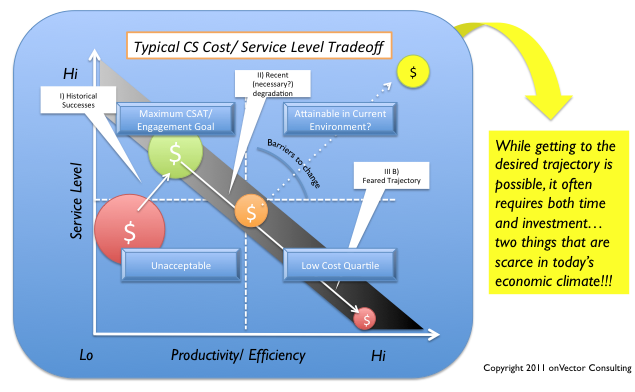





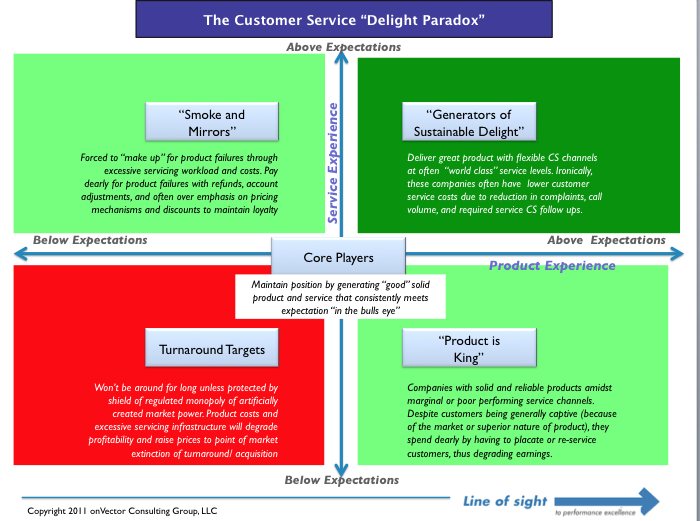 And while, it’s not the “holy grail” on the chart above, operating in the cross hairs (“core players”) can actually be a pretty safe place to play. It won’t earn you much in the way of lagniappe or high levels of customer “delight”, but there is something to be said for consistently meeting both expectations ALL THE TIME. Customers value that more than we often think. Look no further than Southwest Airlines and McDonald’s for examples in this domain.
And while, it’s not the “holy grail” on the chart above, operating in the cross hairs (“core players”) can actually be a pretty safe place to play. It won’t earn you much in the way of lagniappe or high levels of customer “delight”, but there is something to be said for consistently meeting both expectations ALL THE TIME. Customers value that more than we often think. Look no further than Southwest Airlines and McDonald’s for examples in this domain.



 Analysis– When many companies hear the word “analysis”, they go straight to thinking about how they can better “work the data” they have. They begin by taking their scorecard down a few layers. The word “drill down” becomes synonymous with “analysis”. However, while they each are critical activities, they play very separate roles in the process. The act of “drilling down” (slicing data between plants, operating regions, time periods, etc.) will give you some good indication where problems exist. But it is not “real analysis” that will get you very far down the path of defining root causes and ultimately bettersolutions. And often, it’s why we get stuck at this level. Continuous spinning of the “cube” gets you no closer to the solution unless you get there by accident. And that is certainly the long way home. Good analysis starts with good questions. It takes you into the generation of a hypothesis which you may test, change and retest several times. It more often than not takes you into collecting data that may not (and perhaps should not) reside in your scorecard and dashboard. It requires sampling events and testing your hypotheses. And it often involves modeling of causal factors and drivers. But it all starts with good questions. When we refer to “spending more time in the problem”, this is what we’re talking about. Not merely spinning the scorecard around its multiple dimensions to see what solutions “emerge”.
Analysis– When many companies hear the word “analysis”, they go straight to thinking about how they can better “work the data” they have. They begin by taking their scorecard down a few layers. The word “drill down” becomes synonymous with “analysis”. However, while they each are critical activities, they play very separate roles in the process. The act of “drilling down” (slicing data between plants, operating regions, time periods, etc.) will give you some good indication where problems exist. But it is not “real analysis” that will get you very far down the path of defining root causes and ultimately bettersolutions. And often, it’s why we get stuck at this level. Continuous spinning of the “cube” gets you no closer to the solution unless you get there by accident. And that is certainly the long way home. Good analysis starts with good questions. It takes you into the generation of a hypothesis which you may test, change and retest several times. It more often than not takes you into collecting data that may not (and perhaps should not) reside in your scorecard and dashboard. It requires sampling events and testing your hypotheses. And it often involves modeling of causal factors and drivers. But it all starts with good questions. When we refer to “spending more time in the problem”, this is what we’re talking about. Not merely spinning the scorecard around its multiple dimensions to see what solutions “emerge”.